 Azure
Azure
Benefits of Cloud Computing
In this article, we will learn about the benefits or advantages of the Cloud Computing
Total Views: 2391
There are several advantages/benefits of Cloud Computing, out of which few are mentioned below:
1. Cost Effective: As we know that setting up the on-premises IT infrastructure can be extremely expensive as it requires IT hardware, Software & Licenses, and resources i.e., Staff who can maintain the servers. Either you use or don’t use the resource, you need to pay for the maintenance of the IT Infrastructure. This type of expenditure to acquire and maintain the assets is known as Capital Expenditure (CapEx). Several Companies are shifting towards the Cloud Service like Azure as you only need to pay for what you use means to pay for the operational cost also known as Operational Expenditure (OpEx). For example, instead of setting up your own server, you can create and use a Virtual Machine on the cloud. The shift from CapEx to the OpEx model saves a lot of money.
Storage is also a good example of Economy of Scale. Cloud Providers like Microsoft, Amazon purchase a very large amount of Storage hardware, etc. at a very low price as they purchase the hardware in the bulk. They pass that discount to the customers which makes it cheaper rather than having on-premises storage infrastructure.
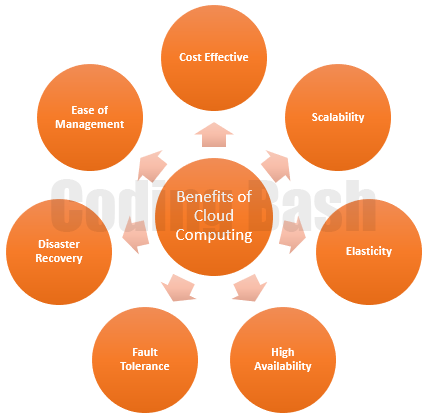
2. Scalability: Scalability is the ability to increase the computing resources based on the demand or usage. For example, on eCommerce websites, during the sale, there is a sudden rise in traffic as compared to the normal days. To handle that traffic, they add multiple servers to manage that traffic. This is an example of Horizontal Scaling. In cloud services, you can easily add more resources like servers, etc. know as Scale-out, and can remove them when not required know as Scale-in.
You can also increase CPUs, RAM, etc. any time based upon the resource utilization known as Scale-up. Once you think that you don’t need the extra processor or memory, you can Scale down the resources as well. Adjusting the capacity of the existing resources is an example of Vertical Scaling. Vertical and Horizontal scaling can be done manually by taking action as per your requirement.
3. Elasticity: In Cloud Computing, you can automate the scaling process based on a set of parameters like based on CPU usage, Memory usage, Storage usage. When the resource utilization reaches the configured threshold limit, it auto-scales the resource as per the rule defined. In Azure, Autoscale is the Azure service that helps in Autoscaling the cloud resources on Azure.
4. High Availability: There can be several reasons due to which a service can be unavailable. It might be due to a network issue at the cloud provider, or any issue at the server level. Cloud computing services are highly available which generally come with SLA that stands for Service Level Agreement (a bond between the cloud provider and the user). Suppose a service which came with 99.9% SLA. It means service will be guaranteed available for 99.9 % for a period. If the service failed to do so, then credit is provided to the user who is using those services. In case you are facing a performance issue but cloud services are available then that will not be considered in SLA.
5. Fault Tolerance: Fault Tolerance enables a system to perform its function even after the failure of a component. For example, Suppose I have one web server. In case any component of that server is failed, my entire web server will be down. To make it fault-tolerant, I will add another web server and balance the traffic between them. In case any server is down, another web server still keeps serving the web request.
6. Disaster Recovery: Disaster Recovery is a strategy to recover the data and the resources after being hit by a disaster. As we saw in fault tolerance, it applies when a component failure occurs. Disaster recovery applies when the failure of multiple systems occurs at the same time. For example, Your company has a data center in the US that is hit by a Tornado or any disaster, destroying all infrastructure, service, etc. With Disaster Recovery, you can either keep the replica or backup in different regions so that in case of any disaster, you can use the replica or backup to keep running the business without any data major issue. Disaster Recovery strategies might be different for different companies depending upon the size of the company. The small company keeps backup of the data as a disaster recovery strategy whereas big companies have a complex strategy for disaster recovery.
7. Ease of Management: Cloud Providers provide an online portal from where you can directly manage computing services, data storage, network, application resources without the involvement of any third person.
